PPT The Binomial Distribution PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4478273
Binomial Probability Distribution Table This table shows the probability of x successes in n independent trials, each with probability of success p . n x 2 0.01 0.9801 1 0.0198 2 0.0001 3 0.9703 1 0.0294 2 0.0003 3 4 0.9606 1 0.0388 2 0.0006 3 0.05 0.9025 0.0950 0.0025 0.8574 0.1354 0.0071 0.0001 0.8145 0.1715 0.0135

Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart Excel Template
In general, the mean of a binomial distribution with parameters N (the number of trials) and π (the probability of success on each trial) is: (5.7.11) μ = N π. where μ is the mean of the binomial distribution. The variance of the binomial distribution is: (5.7.12) σ 2 = N π ( 1 − π)

Solved Let X denote a random variable that has a binomial
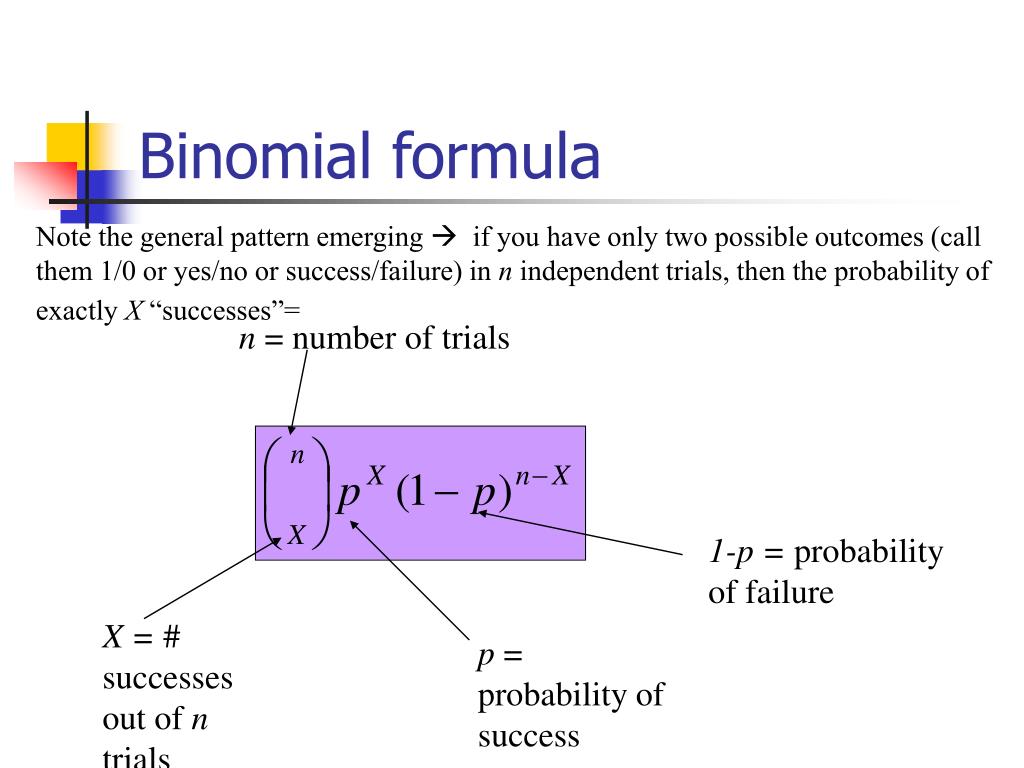
The binomial distribution describes the probability of obtaining k successes in n binomial experiments. If a random variable X follows a binomial distribution, then the probability that X = k successes can be found by the following formula: P (X=k) = nCk * pk * (1-p)n-k where: n: number of trials k: number of successes
Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart Excel Template
A binomial distribution can be thought of as simply the probability of a SUCCESS or FAILURE outcome in an experiment or survey that is repeated multiple times. The binomial is a type of distribution that has two possible outcomes (the prefix " bi " means two, or twice).

Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart Excel Template
This is illustrated in Table 9.3, using the binomial distribution and the normal distribution as examples. Let's have a look at what all four functions do. Firstly, all four versions of the function require you to specify the size and prob arguments: no matter what you're trying to get R to calculate, it needs to know what the parameters.

Peter's Statistics Crash Course
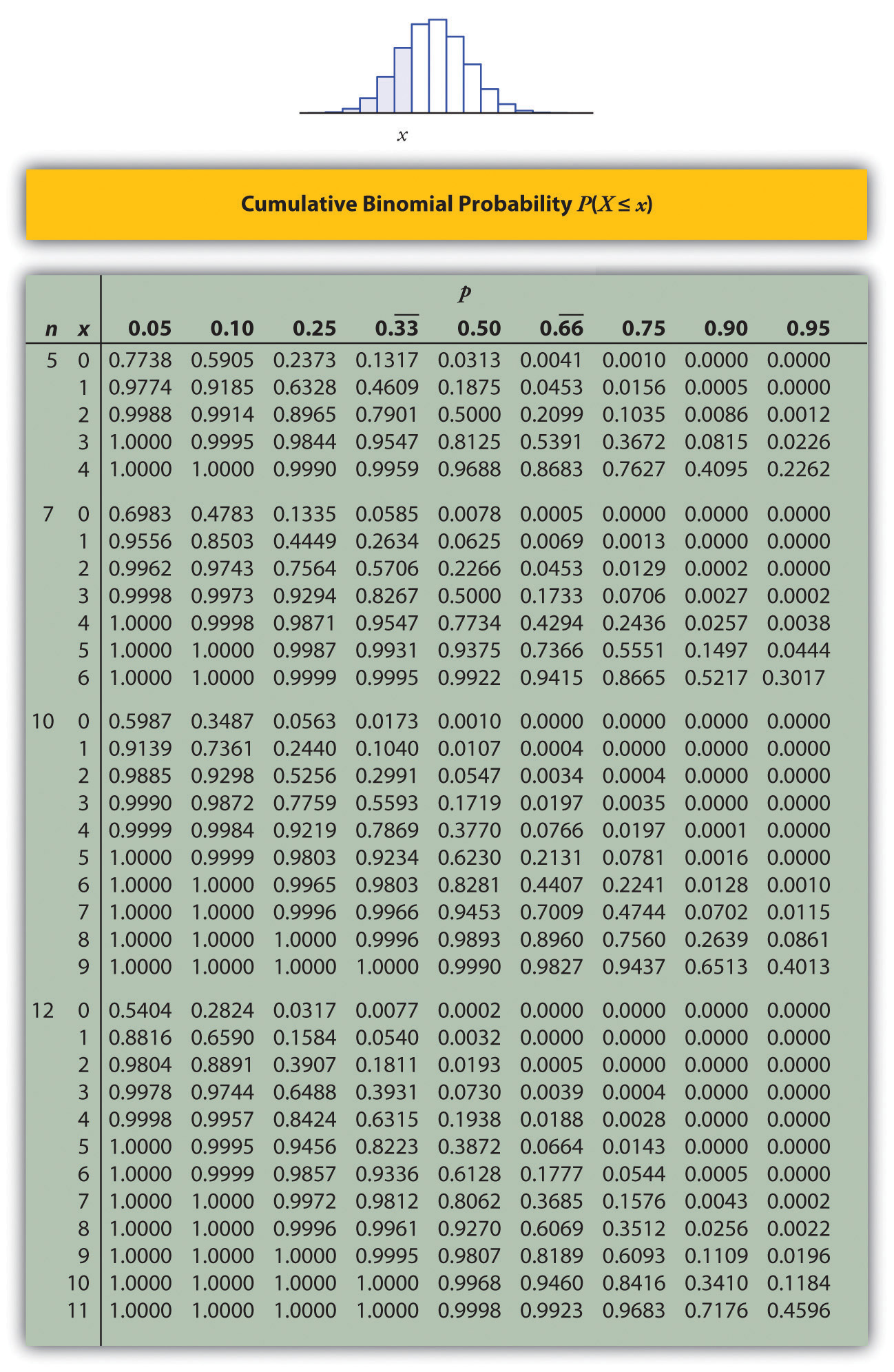
To learn how to determine binomial probabilities using a standard cumulative binomial probability table when p is greater than 0.5. To understand the effect on the parameters n and p on the shape of a binomial distribution. To derive formulas for the mean and variance of a binomial random variable. To understand the steps involved in each of.
Binomial Distribution
This is a binomial problem because there is only a success or a failure, and there are a definite number of trials. The probability of a success stays the same for each trial. Notation for the Binomial: B = B = Binomial Probability Distribution Function. X ∼ B(n, p) (4.4.4) (4.4.4) X ∼ B ( n, p)

pgfmath Binomial distribution in table TeX LaTeX Stack Exchange
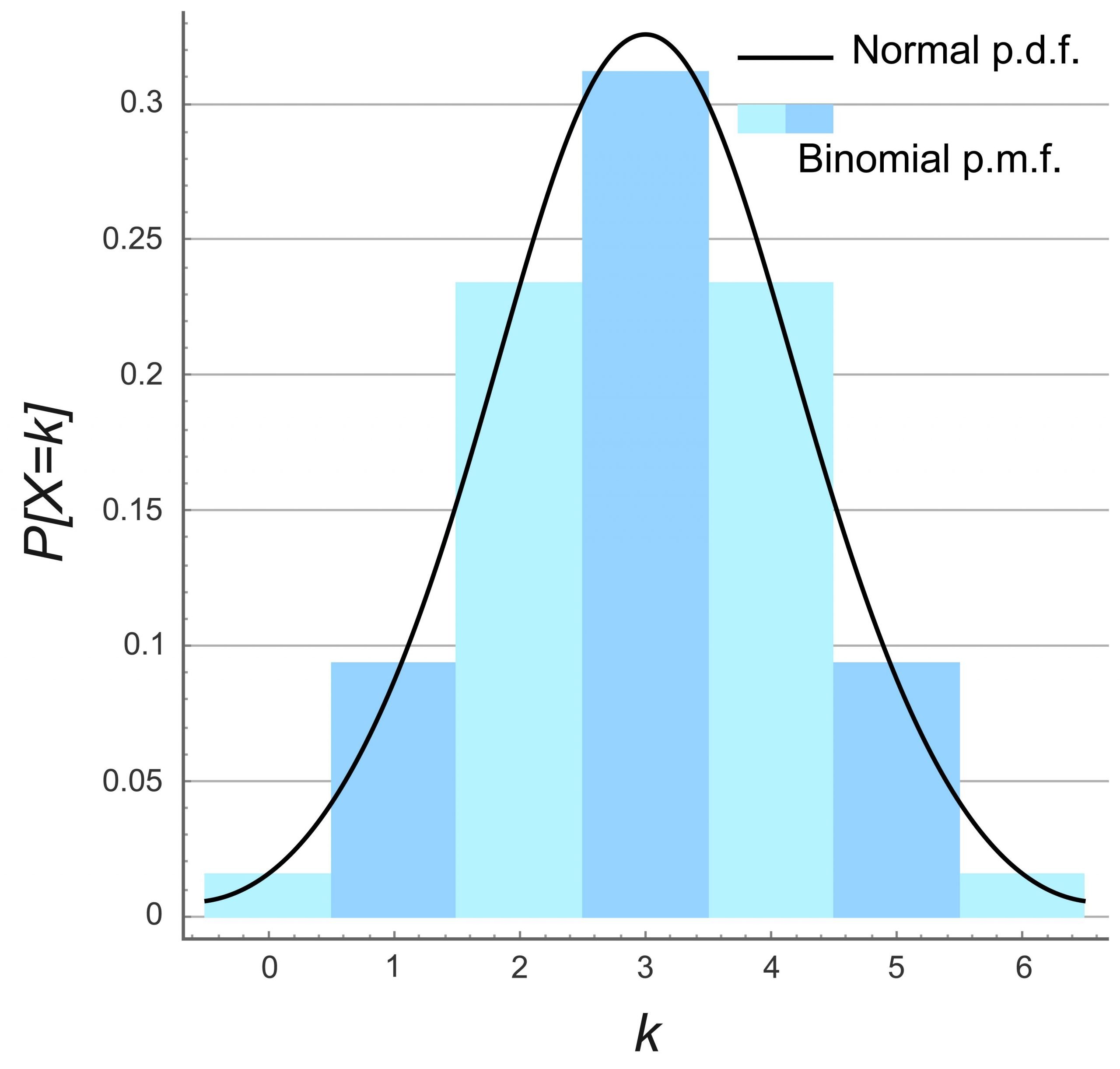
The probability distribution of a binomial random variable is called a binomial distribution . Suppose we flip a coin two times and count the number of heads (successes). The binomial random variable is the number of heads, which can take on values of 0, 1, or 2. The binomial distribution is presented below. 0.50.
-1.png)
[Solved] Consider a binomial distribution with 10 SolutionInn
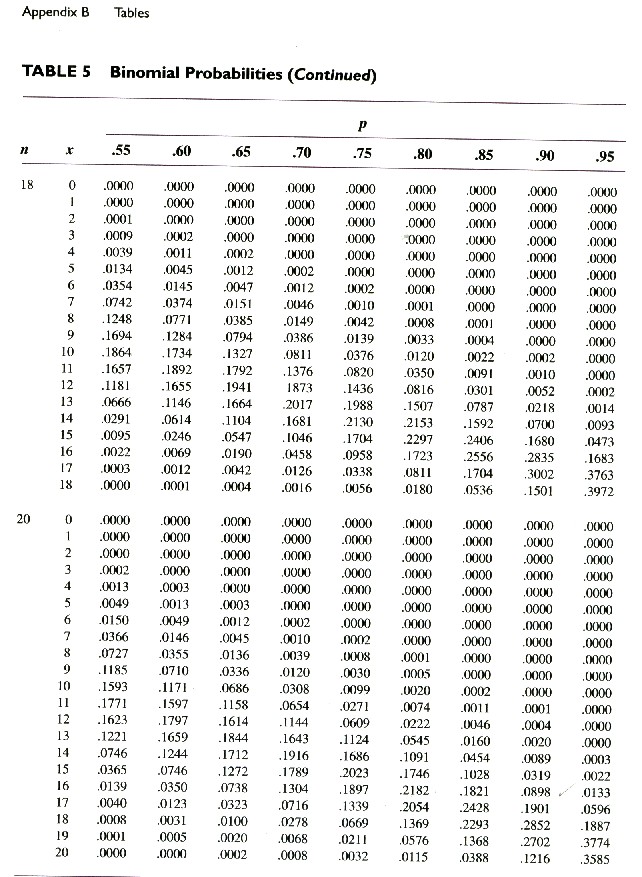
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent experiments,. In creating reference tables for binomial distribution probability, usually the table is filled in up to n/2 values.
Solved X is a binomial random variable with parameters n =
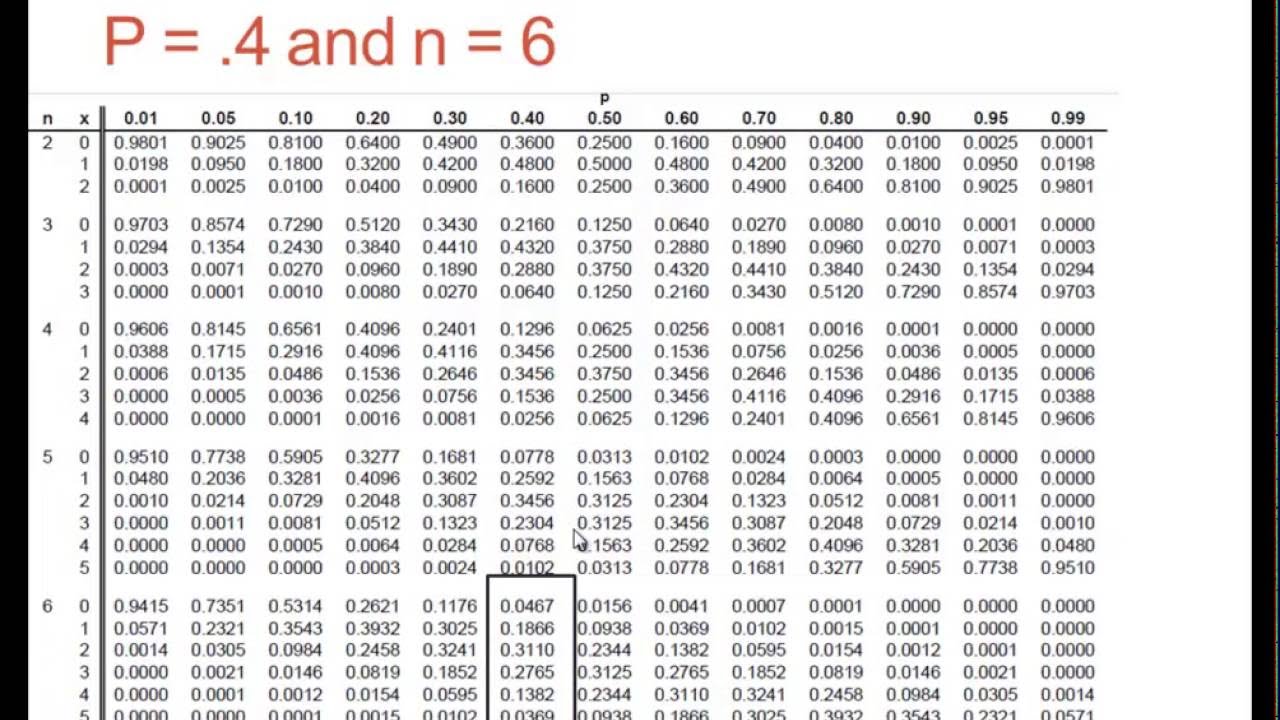
The distribution of this type of variable, referred to as the binomial distribution, is completely determined by two parameters: n and p. Here n is the number of trials and p is the probability of success. The tables below are for n = 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. The probabilities in each are rounded to three decimal places.
Probability Distribution
So, we can treat the actual World Series as a binomial experiment with seven trials. If W W is the number of games won by the Reds, the probability that the Reds win the World Series is P(W ≥ 4) P ( W ≥ 4). Using the techniques from the last example, we get P(Reds win the series) = 0.8002 P ( Reds win the series) = 0.8002.
Binomial Table PDF
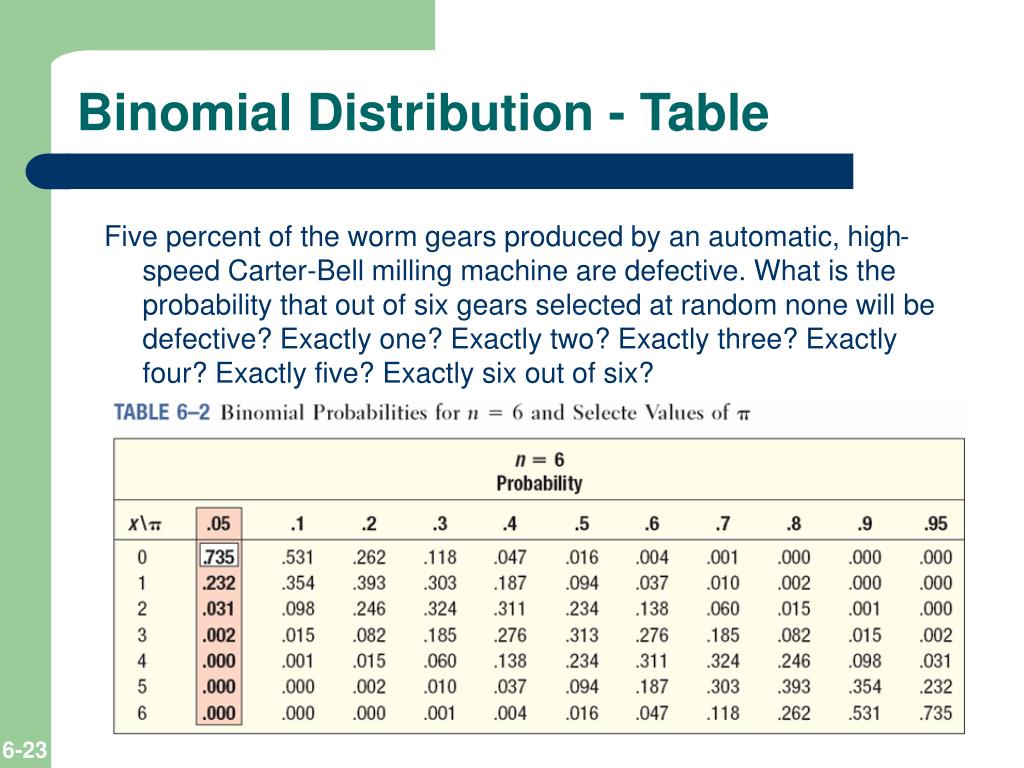
Binomial Distribution Table p n x 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 0.95 1 2
PPT Discrete Probability Distributions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6187022
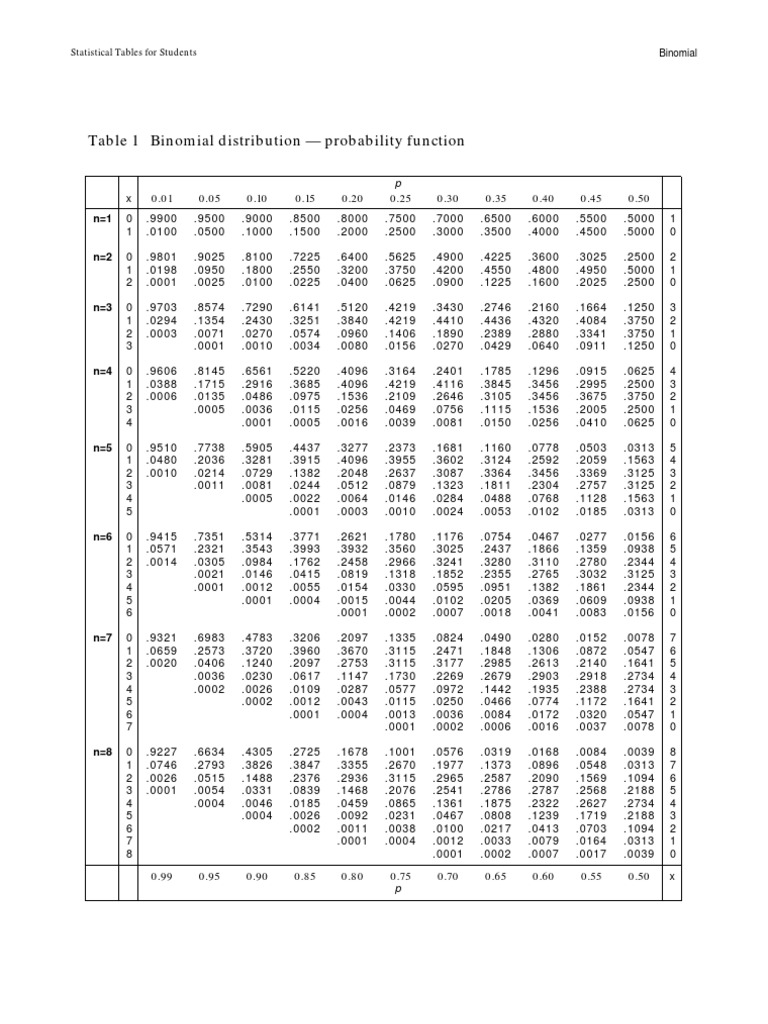
Statistical Tables for Students Binomial Table 1 Binomial distribution — probability function p x 0.01 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 .300.35 .400.45 0.50
Peter's Statistics Crash Course
This binomial distribution table has the most common cumulative probabilities listed for n. Homework or test problems with binomial distributions should give you a number of trials, called n. Click the link below that corresponds to the n from your problem to take you to the correct table, or scroll down to find the n you need. n = 3: n = 4:

PPT Binomial Distributions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5761100
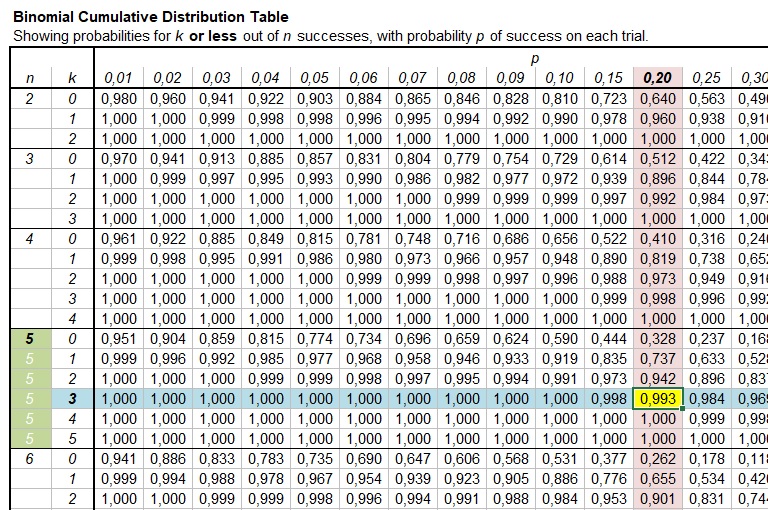
Using Binomial Tables Even for a relatively small value of n, the computation of binomial probabilities can be tedious. Appendix Table A.1 tabulates the cdf F(x) = P(X x) for n = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 in combination with selected values of p. Various other probabilities can then be calculated using the proposition on cdf's.

How to Read the Binomial Distribution Table Statology
To learn how to determine binomial probabilities using a standard cumulative binomial probability table when \(p\) is greater than 0.5. To understand the effect on the parameters \(n\) and \(p\) on the shape of a binomial distribution.